- *设计思维*作为一种正式的方法论,[自 20 世纪 60 年代以来已跨多个学科发展](https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/design-thinking-get-a-quick-overview-of-the-history),并且通常与设计和咨询公司 [IDEO](https://designthinking.ideo.com/) 和斯坦福大学联系在一起设计学院([d.school](https://dschool.stanford.edu/))。
- 设计思维将人置于每个流程的中心,并鼓励设计师放弃假设。例如,[设计思维](https://www.codecademy.com/resources/docs/uiux/design-methodologies/design-thinking)方法不是设计一款新的儿童牙刷,而是将“如何清洁牙齿”定义为问题,并探索各种解决方案。
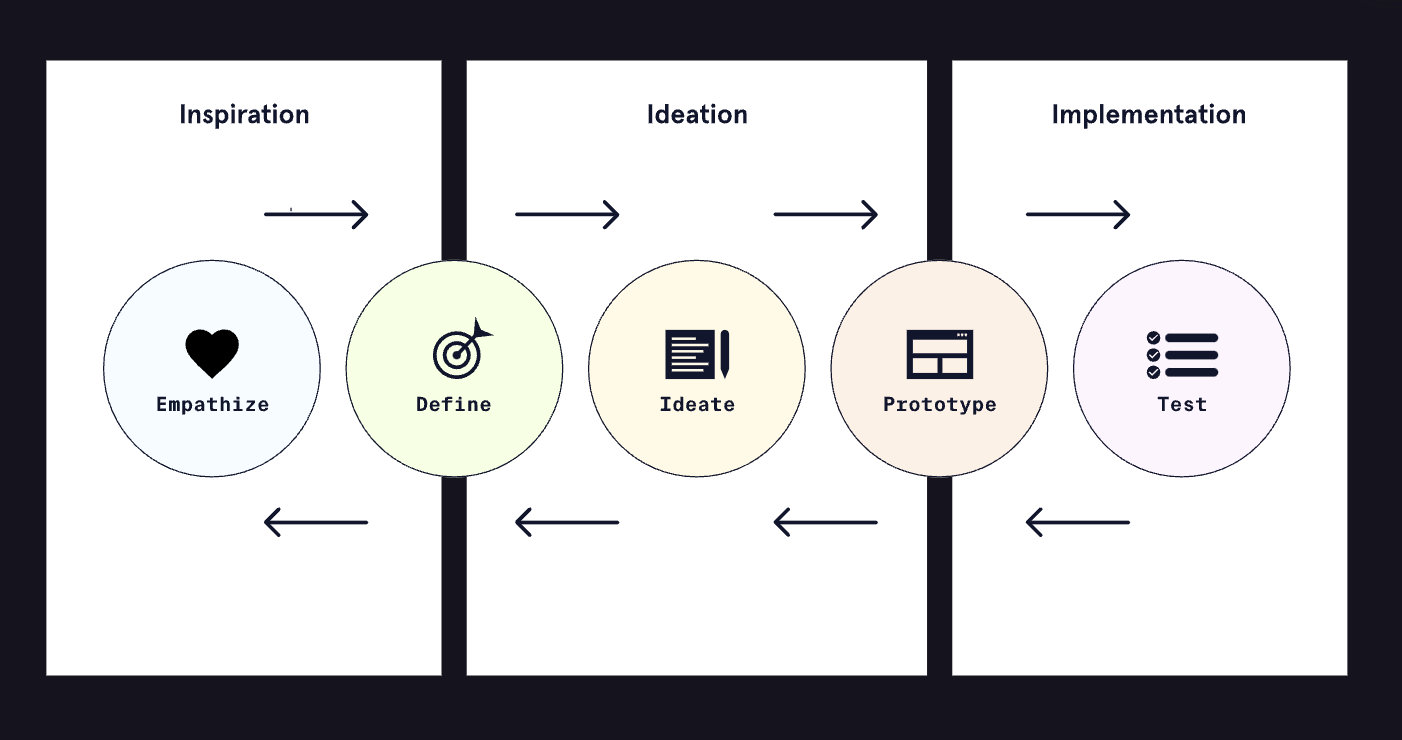
- 设计思维的核心活动是==灵感、构思和实施==,发生在该过程的五个阶段:
- **Empathize**: Understand the user and the landscape.**同理心**:了解用户和环境。
- **Define**: Define the problem and align with business goals and user needs.**定义**:定义问题并与业务目标和用户需求保持一致。
- **Ideate**: Generate a range of ideas for possible solutions, emphasizing creativity.**创意**:为可能的解决方案产生一系列想法,强调创造力。
- **Prototype**: Explore potential solutions by creating prototypes of the product to gather feedback.**原型**:通过创建产品原型来收集反馈来探索潜在的解决方案。
- **Test**: Test the best solutions developed during prototyping. Prototyping or testing may lead to redefining the problem altogether. As with the other processes we’ve covered, this is an iterative cycle.**测试**:测试原型设计过程中开发的最佳解决方案。原型设计或测试可能会导致完全重新定义问题。与我们介绍的其他流程一样,这是一个迭代循环。
-